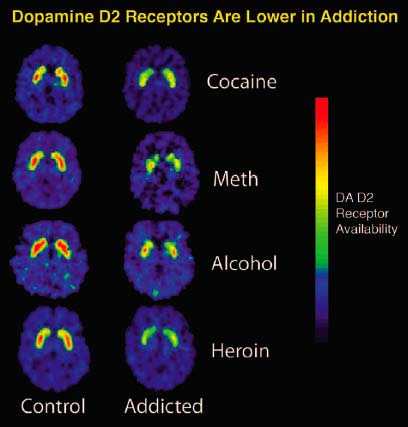
Courtesy National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institute of Health
The rewarding effects of drugs of abuse come from large and rapid upsurges in dopamine, a neurochemical critical to stimulating feelings of pleasure and to motivating behavior. The rapid dopamine “rush” from drugs of abuse mimics but greatly exceeds in intensity and duration the feelings that occur in response to such pleasurable stimuli as the sight or smell of food, for example. Repeated exposure to large, drug-induced dopamine surges has the insidious consequence of ultimately blunting the response of the dopamine system to everyday stimuli. Thus the drug disturbs a person’s normal hierarchy.



